What are Intramedullary Nails?
Intramedullary nails are metal rods that are inserted into the hollow marrow (medullary) cavity of a broken bone to align and stabilize the fracture during healing. This technique is commonly used for fractures of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). It may also be used elsewhere such as the humerus (arm bone) or in the radius and ulna (forearm bones). Because they are located within the bone, they allow for earlier resumption of weight bearing.
What patient can expect before surgery?
- Clinical examination to recognize the injury and presence of any additional injuries that require treatment
- Primary stabilization of the patient is a multi-disciplinary process that aims to ensure that the injured patient is adequately treated for all additional injuries, especially head/chest/abdomen/spine and pelvis injuries. Some patients may require admission/transfer to the intensive care unit (ICU) for optimization
- X-ray of the affected limb to evaluate the fracture configuration and extent
- CT scan of the limb may be required to better understand the fracture configuration in some patients
- Preoperative physiotherapy assessment focuses on ameliorating secondary complications like bedsores, pulmonary embolisms (blood clots) etc.
- Anaesthesia checkup to recognise potential medical issues that can affect the peri-operative course
- Additional investigations like blood tests, chest Xray, electrocardiogram (ECG) or any other test as determined by the anaesthetist/physician / other medical specialists as being essential for surgery
- Patients who suffer high-energy injuries often require a multidisciplinary approach that also involves the physician, general surgeon, plastic surgeon, anaesthetist and other allied medical fields.
- If required some patients may require to be started on blood thinners (anticoagulants) because patients with lower limb fractures are at a higher risk of developing blood clots within the circulation which may then migrate to the heart or the lungs and cause perioperative complications.
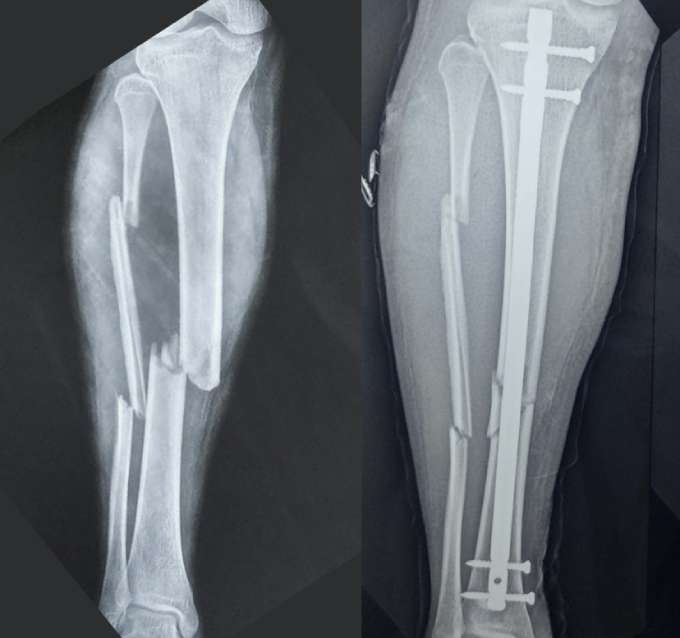
The Procedure
The anesthetist in consultation with the patient usually decides the type of anesthesia given for the surgery.
- The fracture is first realigned into the proper position.
- A small incision is made and the medullary canal is prepared to receive the implant. Once adequately prepared, the IM nail is inserted into the marrow cavity across the fracture site.
- The nail is secured with interlocking screws at each end to keep it in place.
- The incision is closed with stitches or staples.
- The entire procedure is performed with the guidance of a special X-ray machine that allows the surgery to be done without directly visualizing the fracture thus allowing for a minimally invasive procedure.
Benefits of IM Nailing
- Provides rigid fracture fixation for better alignment and healing
- Minimally invasive with smaller incisions than plates/screws
- Allows for immediate weight bearing as tolerated
- Reduces risk of complications like infection and soft tissue damage due to decreased need for extensive open surgical exposures
- Preserves more of the blood supply to the bone
Recovery Process
- A splint or brace may be used initially for protection and pain relief
- Early physical therapy focuses on regaining mobility and strength
- Weight-bearing is allowed as guided by your doctor
- Most patients can resume normal activities within 3-6 months
Risks & Complications:
As with any surgery, risks include bleeding, infection, nerve injury, and issues with bone healing. Complications are relatively rare when performed by an experienced surgeon.
IM nailing is an effective method to stabilize and properly align broken long bones, allowing them to heal in the correct position. Early mobilization and a dedicated rehabilitation program facilitate optimal recovery.


